 |
| Small and the pH range is narrow |
Intracellular pH homeostasis plays an important role in life activities such as the proliferation and death of cells, drug resistance, phagocytosis, and endocytosis. In cells, organelles have various pH values; for example, lysosomes and endosomes are sub-acidic, while active mitochondria and cytosol are sub-alkaline. Abnormal intracellular pH changes are known to be associated with cell dysfunction as well as a variety of diseases such as cancer and Alzheimer's disease. Recently, it has been reported that mitophagy, a physiological effect that causes extensive pH changes in mitochondria (pH8~4) and removes it, is closely related to the state of the disease.
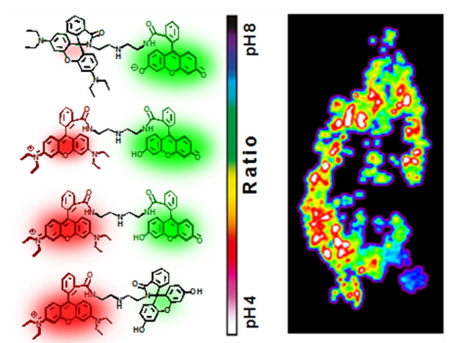
In particular, research into the development of fluorescence, which enables ratio-quantitative self-calibration of two bands of fluorescence, has been promoted to measure pH changes in cells accurately. However, existing fluorescent materials have problems in that wavelength differences between the two bands of fluorescence emission are small and the pH range is narrow.
In order to overcome these problems, the research team has been focusing on the research and development of small molecules with a variety of fluorescent groups in terms of emission and applicable pH values. The team succeeded in measuring ratio-quantitative fluorescent changes in intracellular pH values ranging from pH4 to pH8 by generating a synthetic single molecule consisting of fluorescein emitting fluorescence in neutral-alkaline environment (absorption / emission, 563/572nm) and rhodamine releasing fluorescence in acidity (absorption / emission, 563/572nm). As a result, the abnormal changes in intracellular pH values could be measured effectively during various drug treatments such as H2O2 and N-acetylcysteine.
This research is expected to make significant contributions to the diagnosis and development of disease treatment through the optimization of detection targets by enabling precise quantitative measurement and monitoring of abnormal pH changes.
Based on the recognition of its creativeness and excellence, this study was published in June in Angewandte Chemie International Edition (IF = 13.455), which is one of the world’s most prestigious journals in the field of chemistry. In 2009, Professor Kim was selected by the Research Center for Creative Research under the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology and has been actively conducting research since then.




0 Comments